Navigation
Ethylene/air combustion
Several mechanisms are presented in this section, sorted out in decending order of complexity :
- Detailed mechanisms :
The detailed mechanisms developped by Prof. H. Wang & co-workers (USC II included)
A 32 species skeletal mechanism developped by Dr T. Lu & co-workers
- Analytically reduced mechanisms :
A 22 species reduced mechanism developped by Dr T. Lu & co-workers
A 19 species reduced mechanism developped by Dr T. Lu & co-workers
A 18 transported species mechanism derived with YARC (with associated skeletal mechanism)
- Global mechanisms :
You can find the datas provied on this page on the online database
Please, note that unless explicitly specified, the output files provided in this website are a mean of comparison and are not necessarily formatted to be used as a restart file for cantera/can2av/...
Detailed mechanisms
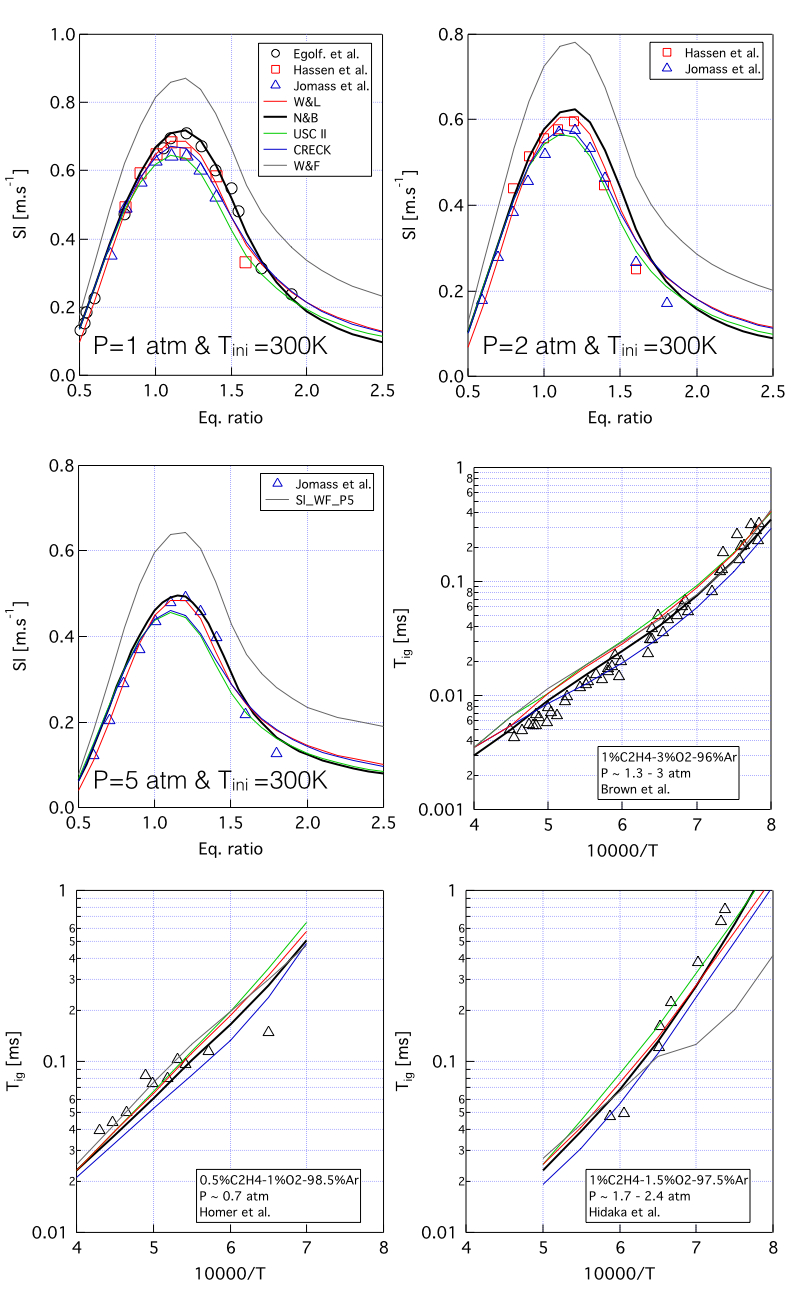
The detailed mechanisms developped by Prof. H. Wang & co-workers
Two schemes in particular are dedicated to the combustion of ethylene and acetylene, with a focus on soot formation. Those schemes are heavily detailed. Information about them can be found on the website of Pr. Wang .
- 1D freely-propagating premixed flame
- Wang-Laskin mechanism ("W&L"): Standard conditions : 300K - 1bar - phi=1 (restart xml file)
- Wang Frenklach mechanism ("W&F"). This mechanism gives very wrong predictions of laminar flame speed !: Standard conditions : 300K - 1bar - phi=1
Data files are provided below:
The USC II mechanism is a more general H2/CO/C1-C4 kinetic model, often used for ethylene combustion in the literature. Information can be found on this dedicated page .
- 1D freely-propagating premixed flame
- Standard conditions : 300K - 1bar - phi=1
Data files are provided below (formatted for the AVBP tool can2av):
The UCSD mechanism
The UCSD scheme is a detailed mechanism that can be employed to simulate ethylene combustion in air. It involves 57 species in 268 reactions. The CHEMKIN mechanism file to generate the .cti can be found here, while the CHEMKIN transport and thermo data can be found in there. More info on this web site
- 1D freely-propagating premixed flame
A data file is provided below (can2av formatted):
Comparison between different ethylene-air schemes (including the UCSD mechanism) can be found on this article.
A 32 species skeletal mechanism developped by Dr T. Lu & co-workers
This skeletal scheme is composed of 32 species and 206 reactions. It is based on the comprehensive kinetic model USC II, developped by searchers of the University of Southern California. Information about the skeletal scheme can be found on the website of Dr T. Lu..
- 1D freely-propagating premixed flame
A data file is provided below :
Analytically reduced mechanisms
What differs with those type of mechanisms is that the source term of each species that remain is not expressed anymore as a combination of elementary reaction rates; but rather as a complex relation involving the detailed mechanism's reaction rates as well as the concentration of species that may not be amongst the reduced species set. Those mechanisms are characterized by the retained species, and are not associated with a "real" set of reactions, so that they require a special subroutine to override the classical evaluation of the species' source terms.
A 22 species reduced mechanism developped by Lu
This analytically reduced scheme is composed of 22 species. It is based on the comprehensive kinetic model USC II, developped by searchers of the University of Southern California. Information about the reduced scheme can be found on the website of Dr T. Lu.. The suitable routine to compute the kinetics (CANTERA formatted) is available on this file.
- 1D freely-propagating premixed flame
A data file is provided below :
A 19 species reduced mechanism developped by Lu
This analytically reduced scheme is composed of 19 species. It is based on the comprehensive Qin 2000 kinetic mechanism for C1-C3 . Information about the reduced scheme can be found on the website of Dr T. Lu. (find the suitable kinetic routine on this website).
- 1D freely-propagating premixed flame
A data file is provided below :
A 18 transported species ARC and a 29 species skeletal mechanisms (derived with YARC by Anne Felden)
This analytically reduced scheme is composed of 18 species. It is based on a skeletal mechanism comprised of 29 species and 355 (irreversible) reactions that can be found here, and that was derived based on the comprehensive mechanism by Narayanaswamy and co-workers. More info about the detailed scheme can be found on this website., while files necessary for the reduction with YARC (detailed mechanism, skeletal mechanism in FM format, along with thermo and transport data) can be found in this file.
Note that this mechanism was derived based on laminar premixed flames and auto-ignition at P = 3 bars ! Validations in 1D laminar premixed flames at P = 3 / 5 bars, Tini = 300 K and for a large range of equivalence ratio are available.
Files for the AVBP transport as well as the routine for the computation of the kinetics in CANTERA are available on this file. Additionally, you can find all the necessary files for an AVBP computation, or a FlameMaster computation. Note that this mechanism is already implemented in the latest AVBP releases !
- 1D freely-propagating premixed flame
A data file is provided below, which can be used as an initial guess for the can2av tool :
Global mechanisms
BFER's mechanism
This simplified model involves 6 species in 2 reactions (C2H4 oxidation and CO-CO2 equilibrium). The model has been tested and validated for several equivalence ratio, but is fitted for an operating pressure of 3 bars !
- 1D freely-propagating premixed flame
The following solution file can be downloaded (can2av formatted) :
The evolution of the flame speed of a series of mixtures of C2H4 with air at 300 K, computed with the 2S_C2H4_BFER mechanism, is displayed on the following figure :
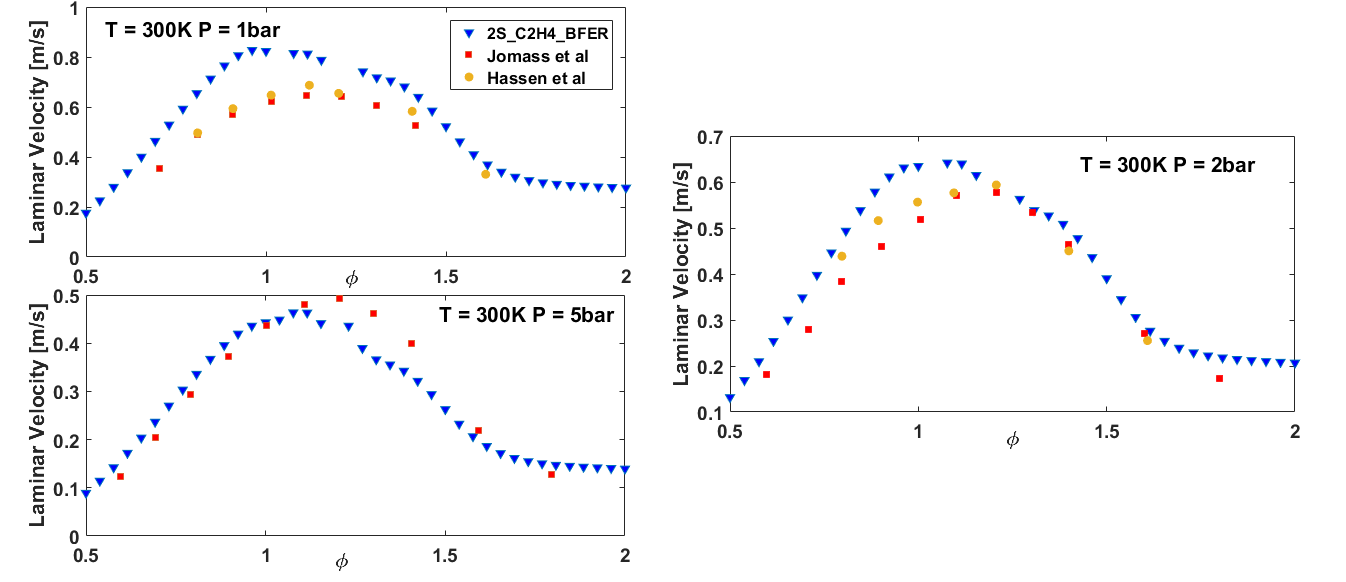
For additional validations of the 2S_C2H4_BFER scheme in terms of laminar velocity (atmospheric temperature) see this file
In order to compute this mechanism with the AVBP transport model in CANTERA, you will need the input files (.dat) from this current directory (the input_thermo, input_premix and input_pea files are available).